Meredith A. Mathson, Amanda L. Murphy, Maysam M. Ardehali, Roger O. Smith
University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee
ABSTRACT
Over a quarter of Americans have disabilities. The impacts of these disabilities are pronounced in 3 areas: mobility, self-care, and household activities (including meal preparation and housework). Preparing meals at home is a powerful way to reduce the risk of depression, stroke, heart disease, cancer, diabetes, osteoporosis, and inflammatory diseases such as arthritis. Small kitchen appliances play a large role in meal preparation and have the potential to help increase the independence in meal preparation of people with disabilities. Currently, however, almost no guidelines exist to ensure that small kitchen appliances are accessible and usable. This paper discusses the development of the Small Kitchen Appliance Accessibility and Universal Design Information Tool (SKA AUDIT). This tool allows practitioners to score the accessibility and usability of common small kitchen appliance features based on their client’s impairments. The SKA AUDIT assists practitioners and their clients (and potentially the general public) in choosing small kitchen appliances that are more accessible and usable, in accordance with the user’s level of ability.
BACKGROUND
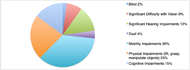
It is estimated that approximately one billion people in the world have a disability; in the United States, 27.2% of the population (85.3 million people) have a disability [1,10]. Of the 85.3 million people, individuals experience disability related to vision, hearing, mobility, object manipulation, and cognition (Fig. 1) [2,3]. The three life areas most impacted by a disability are mobility, self-care, and household activities including meal preparation and housework. Of these categories, household activity is reported to be most affected with 71% of people with disabilities having limitations and difficulties making meals for themselves and their loved ones, especially as age increases [4]. Twelve-million adults cannot complete the task independently, and a strong reason is the lack of accessibility and usability of the small kitchen appliances currently on the market [2].
To date, considering the size of the population with disabilities that challenge meal preparation, a large gap exists to provide accessibility and usability guidelines of commonly used small kitchen appliances. Section 804 of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) guidelines include specifications regarding public or commercial kitchen layout, clear floor space, sink height, storage location, workspace height, dishwasher position, cooktop location, oven relation to workspace, and refrigerator and freezer position. However, there are no guidelines addressing small kitchen appliances [7].
An example of accessible and usable kitchen tools and cookware is the OXO product line that “incorporated plump, resilient handles for twist and push-pull tools like knives and peelers…all handles were oval in cross section, to better distribute forces on the hand and enhance grip...the measuring cups and spoons featured large, high-contrast markings for visibility.” These products help when preparing food and drink, but without the countertop appliances to create a meal, the assistive tools are essentially meaningless [8]. To the best of our knowledge, the only major company selling small kitchen appliances with guidelines related to disability is General Electric (GE). These guidelines are limited to microwave ovens, and only two requirements are published on their website. The first states that the “Maximum high forward reach for controls and operating mechanisms is 48"; maximum low forward reach is 15", and the other states that “controls and operating mechanisms must be operable with one hand and shall not require tight grasping, pinching or twisting of the wrist. The force required to activate controls shall be no more than 5 lbs.” [9]. Though these guidelines act as a start, they encompass a very small percentage of physical disabilities and neglect to address the other categories of disability.
For example, a client with macular degeneration will be unable to read the labels, buttons, or directions on his or her current small kitchen appliances, consequently, making food and drink preparation nearly impossible. The products that have SKA AUDIT scores can be reviewed and recommended to the client by his/her occupational therapist. The results will allow the client to make necessary adaptions and recommendations for the client to continue being independent in the kitchen.
METHODS
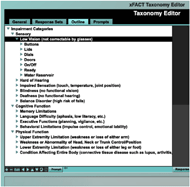
When filling out the AUDIT, users will be able to select the impairment(s) their client has, and the AUDIT will filter out irrelevant questions. The AUDIT will then prompt users to answer accessibility and usability questions about each feature of the small kitchen appliance. Users will be given the opportunity to add comments if desired. An accessibility and usability score will be generated once the user answers all of the relevant questions.
DISCUSSION
Conclusion
The SKA AUDIT is the first of its kind. While GE as one manufacturer applied two ADA standards regarding the accessibility of their microwaves, more needs to be done to ensure people with impairments are able to access and use small kitchen appliances when preparing food [9]. This AUDIT data can help individuals with impairments make informed choices when purchasing small kitchen appliances. The AUDIT addresses features of devices that exist already, and the authors made predictions of potential future features that will increase the usability of small kitchen appliances. Currently, the AUDIT is designed to be used by practitioners to help their clients. Other potential beneficiaries of the results of this audit include engineers, manufacturers, advertisers, retailers, and family members of individuals with impairments.
Limitations
Due to its recent development, the SKA AUDIT has not been used extensively. Additionally, we still need to develop additional versions that include relevant terminology and question structure for stakeholders than therapists. Lastly, due to the vast amount of available small kitchen appliances and constantly changing technology, it was difficult to include every available appliance feature in the AUDIT. To accommodate for this, the authors included and encourage the use of the comment sections throughout the AUDIT.
Future Directions
Following the development of additional versions, we plan on creating a database featuring all products and ratings based on reviews from users from each disability category. The database will allow results to be available to all stakeholders including: consumers, practitioners, manufacturers, standardization organizations, engineers, and more. Further development of this AUDIT will encourage developers to create small kitchen appliances that are more universally designed. Additional questions will be added to the various versions of the SKA AUDIT as new features of small kitchen appliances are developed, and we plan to make accessibility and usability ratings available to all stakeholders.
REFERENCES
[1] Taylor, D. M. (2018). Americans with disabilities: 2014. United States Census Bureau. Retrieved from https://www.census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2018/demo/p70-152.pdf
[2] US Census Bureau. (2010). Nearly 1 in 5 people have a disability in the U.S., census bureau reports. Retrieved from https://www.census.gov/newsroom/releases/archives/miscellaneous/cb12-134.html
[3] Bialik, K. (2017). 7 facts about Americans with disabilities. Pew Research Center. Retrieved from http://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2017/07/27/7-facts-about-americans-with-disabilities/
[4] Colby, S. L. & Ortman, J. M. (2014). The baby boom cohort in the United States: 2012 to 2060. United States Census Bureau. Retrieved from https://www.census.gov/prod/2014pubs/p25-1141.pdf
[5] Stiles, K. (2015). Nourishment of mind, body, and spirit. Association of Nutrition & Foodservice Professionals (ANFP). Retrieved from http://www.anfponline.org/docs/default-source/legacy-docs/mn/documents/111a-cooking-to-save-your-life.pdf?sfvrsn=0
[6] Durant, S. (2017). Transportation difficulties keep over half a million disabled at home. Bureau of Transportation Statistics. Retrieved from https://www.bts.gov/archive/publications/special_reports_and_issue_briefs/issue_briefs/number_03/entire
[7] Department of Justice. (2010). 2010 ADA standards for accessible design. Retrieved from https://www.ada.gov/regs2010/2010ADAStandards/2010ADAstandards.htm#sec8043
[8] NS State University. (2008). Oxo international becomes a universal design icon. The Center for Universal Design. Retrieved from https://projects.ncsu.edu/design/cud/projserv_ps/projects/case_studies/oxo.htm
[9] GE Appliances. (2018). ADA compliant appliances. Retrieved from https://www.geappliances.com/ge/ada-compliant/#mia-microwaves
[10] Barbotte, E., Guillemin, F., Chau, N., & the Lorhandicap Group (2001). Prevalence of impairments,
disabilities, handicaps and quality of life in the general population: A review of recent literature.
Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 79, 1047-1055. Retrieved from https://www.scielosp.
org/scielo.php?pid=S0042-96862001001100008&script=sci_arttext&tlng=es
[11] Marquette University & University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee. (2005). MED-AUDIT impairment categories: Working towards mapping AMI usability. Rehabilitation Engineering Research Center on Accessible Medical Instrumentation. Retrieved from http://www.r2d2.uwm.edu/rerc-ami/archive/impairments.pdf
[12] Cambridge Dictionary. (2019). Meaning of accessibility. Retrieved from https://dictionary.cambridge.org/us/dictionary/english/accessibility
[13] Benton, S. A., & Bove, V. M. (2011). Handbook of Usability Testing: How to Plan, Design, and Conduct Effective Tests. Indianapolis, IN: Wiley Publishing, Inc.